Package of 5 Sessions
- Rs.5,999.00/-
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive mental health disorder that shrinks the brain and because of it, the brain cells die. It declines behavior, thinking, and social skills that can affect the ability of a person to function independently.
 Surabhi Setiya
Surabhi Setiya  01 Jun 2019
01 Jun 2019  Happiness
Happiness  3.3k Reads
3.3k Reads  7 min Read
7 min Read 
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive mental health disorder that shrinks the brain and because of it, the brain cells die. It declines behavior, thinking, and social skills that can affect the ability of a person to function independently.
At the beginning of this disease, a person with Alzheimer's disease starts to forget the recent events. And as the disease increases, it develops severe memory loss and people suffering from this lose the ability to perform everyday tasks. At one point in time, a person can completely lose their memories. The chances of having Alzheimer's disease subsequently increases around the age of 65 years.
Some people think that Alzheimer's disease is a common part of aging. But it is not something that inevitably happens in later life if you also think so then you are wrong. People under the age of 65 also suffer from this disease.
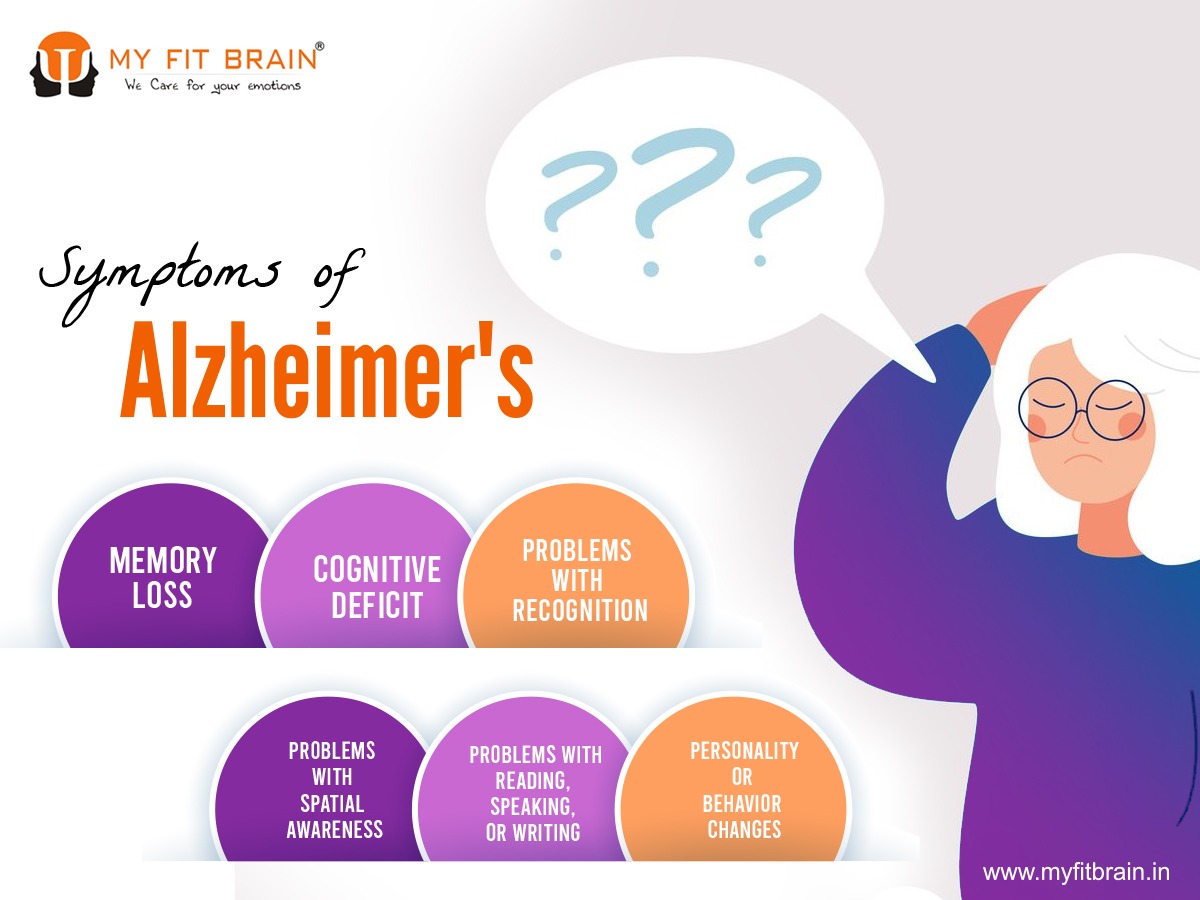

Alzheimer's disease is a progressive condition because its symptoms worsen over time. Memory loss is a major feature and is one of the first symptoms to develop. Symptoms get worse gradually, over months or years. If they develop in hours or days, a person may need therapy, as it may indicate a stroke.
The following are the symptoms of this disease:
A person faces difficulty taking new information and remembering information. This disease can lead to the following conditions:
A person faces problems with complex tasks, reasoning, and decisions. This disease can lead to the following problems:
In this problem, a person becomes less capable to use basic tools and also becomes less capable of recognizing faces or objects. And these problems don't occur due to vision problems.
A person can also face difficulties with their balance, going on a trip, or they also face problems orienting their body to clothes when they wear clothes.
A person faces difficulties in thinking about common words, or they may make errors in speech, spelling, or writing.
A person may face changes in personality and behavior which include:

The range of Alzheimer's disease is from mild to severe. The following are the stages of Alzheimer's disease:
A person with mild Alzheimer's disease face memory problems and cognitive difficulties that includes the following:
In moderate Alzheimer's disease, the parts of the brain damage that are responsible for language, senses, reasoning, and consciousness. The following symptoms can occur in this situation:
In severe Alzheimer's disease, brain tissue shrink to a great extent by plaques and tangents that are presented throughout the brain. The following problems can occur in this stage:
Alzheimer's disease develops when the brain cells die and the brain cell death occurs over time. Researchers do not fully understand why this disease occurs. But the following are the causes that can lead to this disease
The greatest risk factor for this disease is increasing age. While it is not a direct cause of this disease but it can increase the risk of this. This disease mainly occurs in people after the age of 65. This disease doubles after the age of 65 and the risk reaches about one-third after the age of 85.
Another strong cause of this disease is family history. This disease can occur in a person having a parent, brother, or sister with Alzheimer’s. Heredity (genetics), environmental factors, or both, play a very important role when illnesses tend to run in the family.
Two categories of genes tell about the effect of whether this develops a disease:
Risk genes only increase the likelihood of developing a disease but are not guaranteed that it will. Determinant genes The deterministic genes directly become the cause of disease and are guaranteed that it will.
Other risk factors
While age, family history, and heredity are all risk factors for this disease but some clues about other risk factors that we may have in wellness choices, common lifestyle, and effective management of some health conditions. The following are these risk factors:

Doctors perform several tests such as mental, physical, neurological, and imaging tests to determine your diagnosis. Your doctor starts with a mental status test that can help assess your short-term memory, long-term memory. Then he conducts a neurological examination to detect medical problems such as an infection or stroke. Then the brain-imaging study is conducted to create pictures of your brain. The following are the studies for this:
There is no cure for Alzheimer’s disease so your doctor can also recommend medications to reduce your symptoms. Medications such as donepezil (Aricept) or rivastigmine (Exelon) can be prescribed by your doctor for the mild to moderate Alzheimer’s stage. Medications such as donepezil (Aricept) or memantine (Namenda) can be prescribed by your doctor for the moderate to severe Alzheimer’s stage.
To treat Alzheimer's-related symptoms you can also be recommended antidepressants, antioxidant medications, or antipsychotics. The following are the symptoms:
Lifestyle changes can also help you to manage your condition because your doctor can develop some strategies to help you or your loved one:

Finally, I can say that this disease affects your brain, and the symptoms of this become more severe over time. Its common symptoms include language problems, memory loss, and impulsive or unpredictable behavior. There is no current treatment for Alzheimer's disease, but treatments to cure the symptoms are available, and research continues.
The available treatment can't prevent Alzheimer's from advancing but they can only help in improving the quality of life for Alzheimer's and their caregivers. Today, efforts are underway worldwide to find better ways to treat the disease and prevent it from developing.
_1768192276.jpg)

Stress does not always arrive with noise. Sometimes it comes quietly. It si...
 12 Jan 2026
12 Jan 2026  7 min Read
7 min Read 313 Reads
313 Reads _1767765311.jpg)

There is a very specific moment every day that most couples underestimate. ...
 07 Jan 2026
07 Jan 2026  7 min Read
7 min Read 459 Reads
459 Reads _1767610041.jpg)

Many relationships suffer stress, not due to a lack of love or lack of affe...
 05 Jan 2026
05 Jan 2026  7 min Read
7 min Read 425 Reads
425 Reads _1767342715.jpg)

In almost every relationship. If it's between spouses or family members...
 02 Jan 2026
02 Jan 2026  7 min Read
7 min Read 429 Reads
429 Reads 
_1768192276.jpg)
_1767765311.jpg)
_1767610041.jpg)
_1768192276.jpg)
_1767765311.jpg)
_1767610041.jpg)
_1767342715.jpg)